Recognize the real of the fake : tutorial with Orobel
Definition of alloys.
Because of its malleable and ductile pure, gold must be hardened to create gold jewelry at end design. Most jewelry are made of a gold alloy, combination of two or more metals. binary alloy talking to an alloy composed of two different metals and ternary alloy of three different metals.
The most common alloy used in jewelry making is the alloy gold-silver-copper. We will see that following the gold content of jewelry and according to their share in the alloy, the result will be different on the jewel.
The diagram below summarizes the situation thus. Yellow gold, black other metals (silver, copper …)
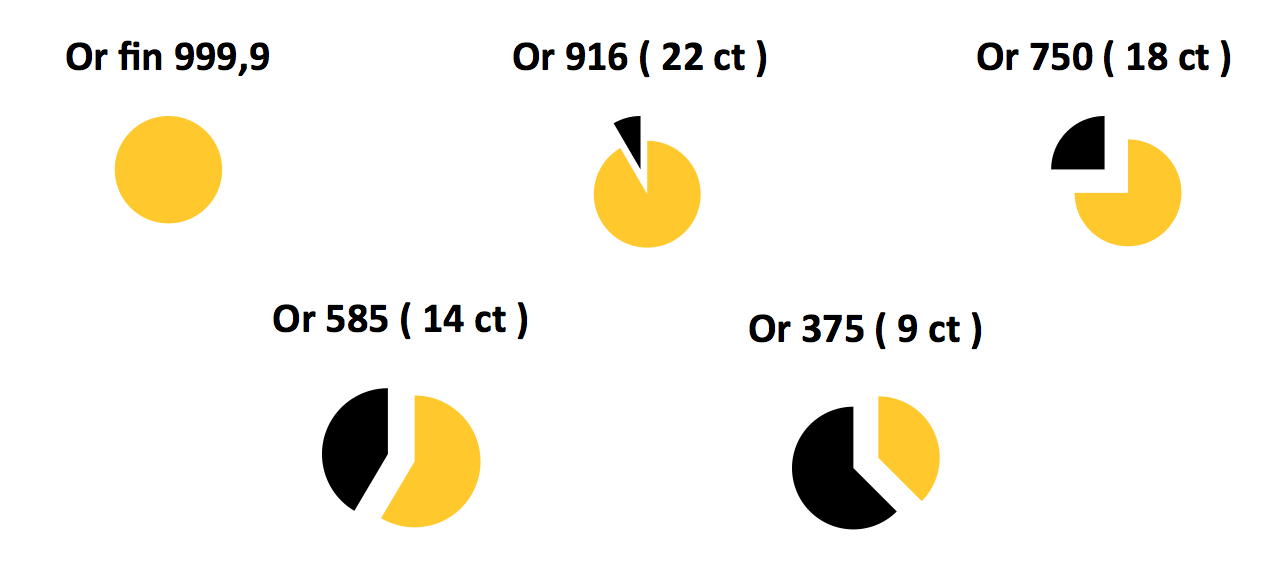
There are two common systems (called punching or marking) to indicate the gold content in jewelry:
- The karat system (Karat or English), abbreviated ct or kt.
- The numeric system as share by thousandths (‰).
These two systems are therefore a measure of purity of precious metal, used in particular for gold. They define the proportion of noble metal in an alloy.
In Europe, the digital system is mostly used for punching but expresses purity in carats jewelry in everyday language.
The karat system.
This measurement system is divided into 24 shares. Thus it means in everyday language by 24 karat gold gold end to 99.9%. 1 karat corresponds to 1 / 24th of the total mass of the alloy (100%), about 4.16%.
18 carat gold means that in 24g alloy, can be found 18g of pure gold. We can then deduce the different percentages for each carat.
- 8 karats : 8 x 4,16 % = 33,3 %
- 9 karats : 9 x 4,16 % = 37,5 %
- 14 karats : 14 x 4,16 % = 58,5 %
- 18 karats : 18x 4,16 % = 75,0 %
- 22 karats : 22 x 4,16 % = 91,6 %
Warning ! Do not confuse karat in jewelry and gemology that means the weight of a stone, 1 karat equal to 0.2 grams.
You now know up to how many % is made your jewelry. However, the European system for measuring the purity of a jewel used is most often the numeric system for punching.
The numeric system
The numeric system expresses the purity of a jewel in parts per mil (‰). For a jewel in 18k, it is therefore more say 75 % but 750 ‰.
The following table summarizes the different strengths of the digital system and their correspondences in karats.
| Numeric system | Titration in % | Correspondance in karats |
| 999 | 99,9 % | 24 karats |
| 916 | 91,6 % | 22 karats |
| 750 | 75,0 % | 18 karats |
| 585 | 58,5 % | 14 karats |
| 375 | 37,5 % | 9 karats |
| 333 | 33,3 % | 8 karats |
Exotic titration
In addition to existing carats, there are also titles of « exotic » jewelry, that is to say, less current but country-specific. Here is a list.
| Origin | Karat | Titration (in ‰) |
|
Asia (China, Nepal, Thaïland, Hong-Kong) |
24 kt | 999 ‰ |
|
Minor Asia, Gulf countries (Dubaï, United Arab Emirates) |
20 kt et 21 kt | 833 ‰ et 875 ‰ |
| Portugal | 19,2 kt | 800 ‰ |
|
United States South Africa |
10 kt et 12 kt | 416 ‰ et 500 ‰ |